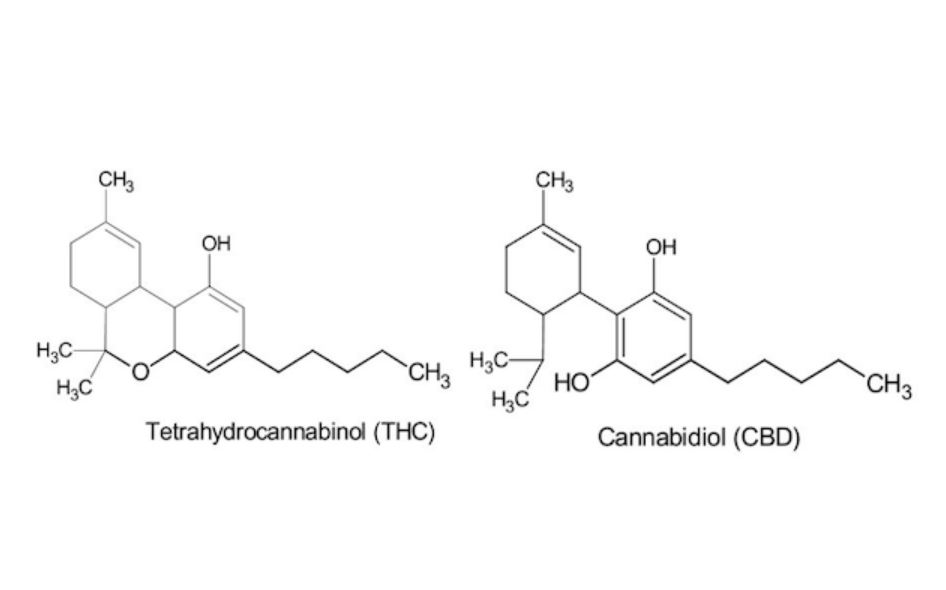
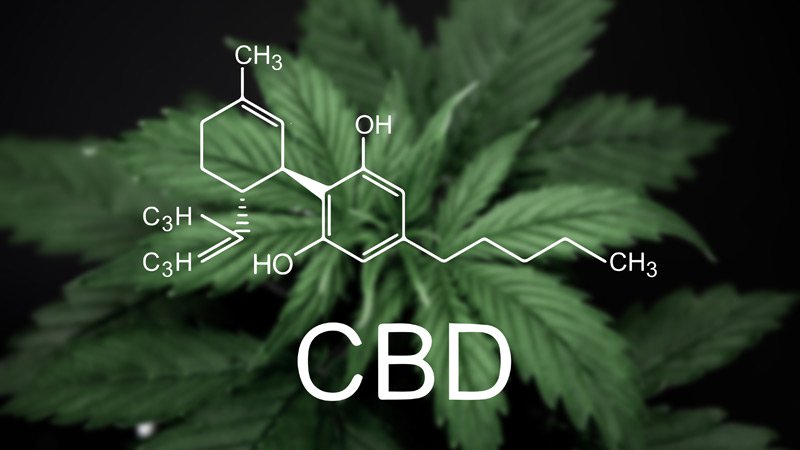
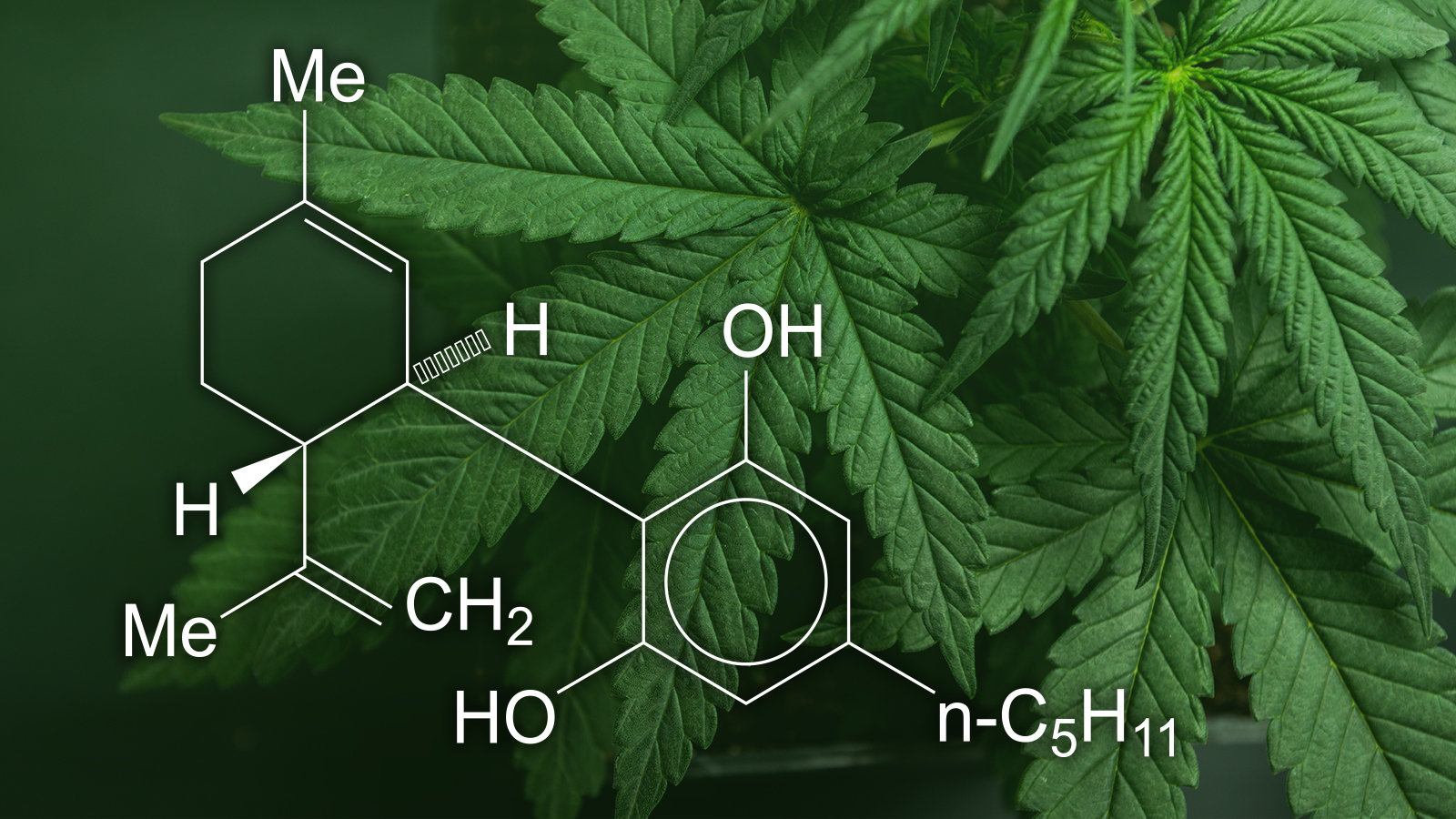
A lot of people ask us, what is a Cannabinoid?
Cannabinoids are organic molecules naturally produced by hemp and cannabis which activate two of the body’s central nervous system receptors: CB1 and CB2.
CB1 receptors are primarily located in the brain, while CB2 receptors are spread throughout the rest of the body. Because CBD does not activate the brain’s CB1 receptors, it is largely non-psychoactive.
Each of the 100+ known cannabinoids have unique receptor interactions, producing individual results. Research has also shown that cannabinoids’ benefits multiply when used together, producing what is called the “entourage effect.”
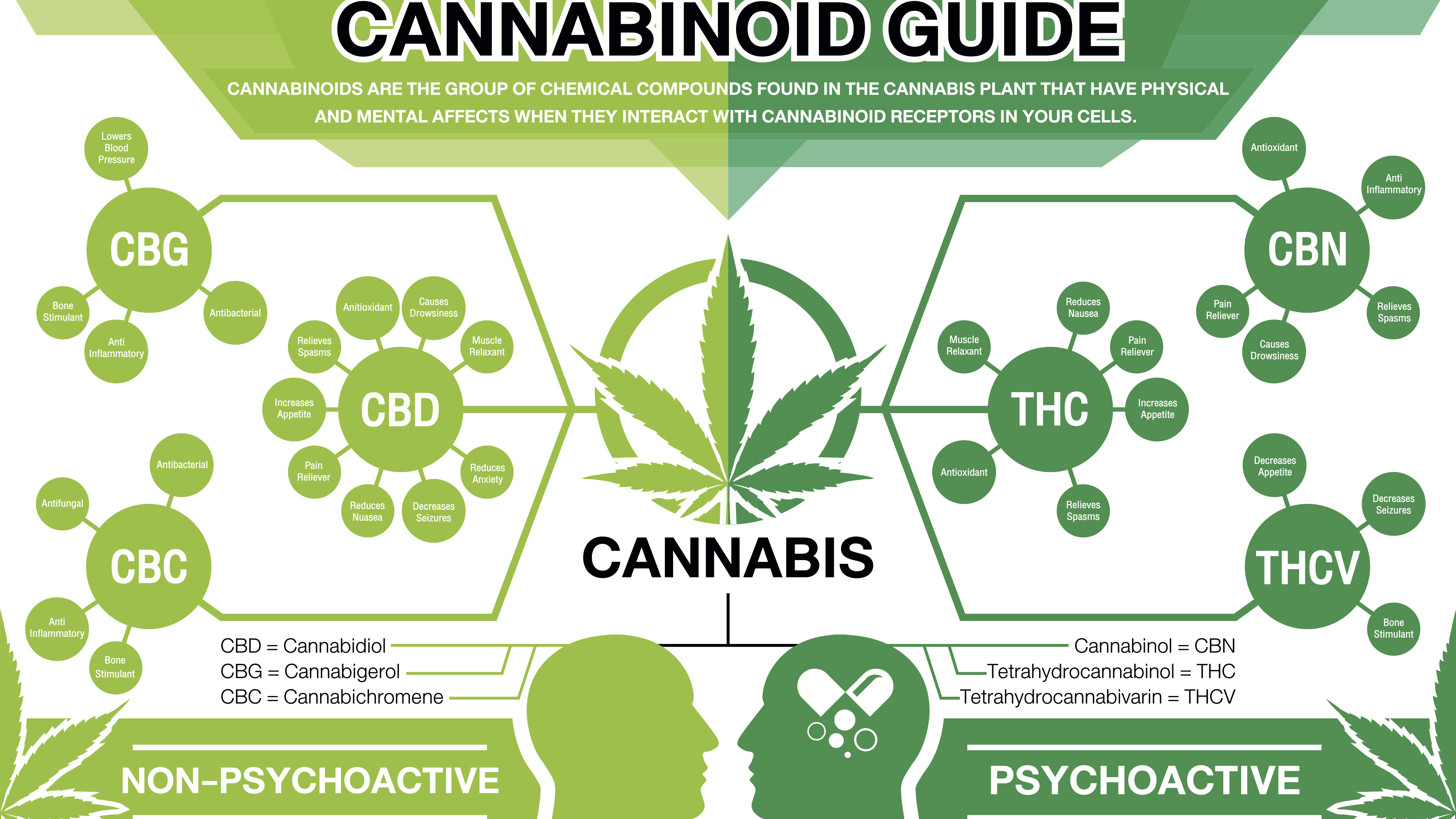
Classes of cannabinoids
The cannabinoids are separated into the following subclasses:
- Cannabigerols (CBG)
- Cannabichromenes (CBC)
- Cannabidiol (CBD)
- Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC)
- Cannabinol (CBN)
- Cannabinodiol (CBDL)
- Other cannabinoids including cannabicyclol (CBL), cannabielsoin (CBE) and cannabitriol (CBT)
Effects of cannabinoids
Cannabinoids exert their effects by interacting with specific cannabinoid receptors present on the surface of cells.
In 1992, a naturally occurring substance in the brain that binds to CB1 was discovered, called anandamide. This cannabinoid-like chemical and others that were later discovered are referred to as endocannabinoids.
The effects of cannabinoids depends on the brain area involved. Effects on the limbic system may alter the memory, cognition and psychomotor performance; effects on the mesolimbic pathway may affect the reward and pleasure responses and pain perception may also be altered.
Differences between cannabinoids
The main way in which the cannabinoids are differentiated is based on their degree of psychoactivity.
For example, CBG, CBC and CBD are not known to be psycholgically active agents whereas THC, CBN and CBDL along with some other cannabinoids are known to have varying degrees of psychoactivity.
The most abundant of the cannabinoids is CBD, which is thought to have anti-anxiety effects, possibly counteracting the psychoactive effects of THC.